Glossary — B
B
Balanced translocation: also known as balanced chromosomal translocation. A chromosomal translocation is a condition caused by two breakages in two chromosomes, followed by an exchange and then a rejoining of the broken ends to produce a new chromosomal arrangement. A balanced translocation happens when there is an even exchange of materials with no genetic information extra or missing.
Biopsy: the taking of a small piece of tissue from a living subject for pathological examination.
Blastocyst: the stage of embryo developpment at which the embryonic cells have differentiated into trophoectoderm (TE) layer and inner cell mass (ICM), with formation of a blastocoelic cavity. The trophoectoderm will form the placenta and fetal membranes, and the fetus will develop from the inner cell mass.
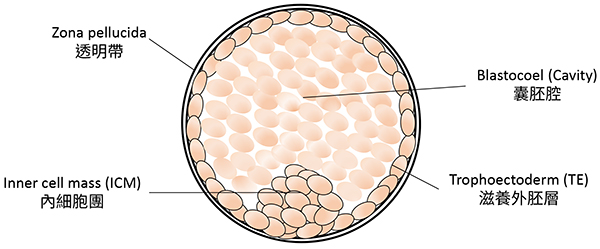
Blastocyst
 scroll right to see more
scroll right to see more
Blastomere: undifferentiated cells of an embryo, formed by cell division of an fertilized egg.