Glossary — ALL
A
Aneuploidy: the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, either in the form of an extra or a missing chromosome. An aneuploidy cell may contain 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46 chromosomes in a healthy human.
Anovulation: absence of ovulation.
Artificial insemination: the introduction of semen into the female uterus or cervix by means other than sexual intercourse.
Assisted hatching (AH): the mechanical, chemical or laser breaching of the zona pellucida to provide a hole through which the embryo can escape and hatch in the uterus.
Assisted reproductive technology (ART): that part of reproductive medicine which deals with means of conception other than normal coitus. ART frequently involves intra-uterine insemination (IUI), in-vitro fertilization (IVF), embryo transfer (ET), cryopreservation and other related procedures.
Asthenozoospermia: reduced sperm motility.
Azoospermia: absence of spermatozoa in the semen.
B
Balanced translocation: also known as balanced chromosomal translocation. A chromosomal translocation is a condition caused by two breakages in two chromosomes, followed by an exchange and then a rejoining of the broken ends to produce a new chromosomal arrangement. A balanced translocation happens when there is an even exchange of materials with no genetic information extra or missing.
Biopsy: the taking of a small piece of tissue from a living subject for pathological examination.
Blastocyst: the stage of embryo developpment at which the embryonic cells have differentiated into trophoectoderm (TE) layer and inner cell mass (ICM), with formation of a blastocoelic cavity. The trophoectoderm will form the placenta and fetal membranes, and the fetus will develop from the inner cell mass.
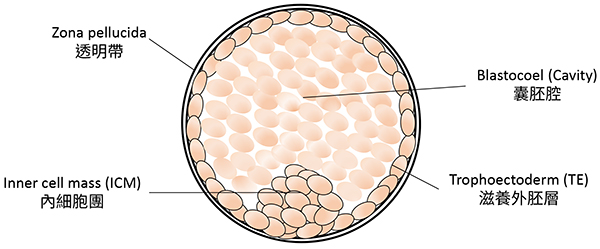
Blastocyst
 scroll right to see more
scroll right to see more
Blastomere: undifferentiated cells of an embryo, formed by cell division of an fertilized egg.
C
Carrier: also known as hereditary carrier, is an individual who has inherited and is capable of passing on a recessive genetic mutation of a disease but usually does not have symptoms of the disease. If a couple carry the same genetic mutation, their offspring will have a 25% chance of having the disease.
Cell: the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all organisms.
Chromosome: the thread-like, darkly staining structures in the cell nucleus which contain the hereditary material – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). All human cells have 23 pairs and a total of 46 chromosomes, except for eggs and sperm which have only 23 chromosomes as a result of meiosis.
Congenital malformation: also known as birth defect, is a condition present at the time of birth which may result in physical, intellectual or developmental disabilities. Congenital malformation may be due to genetic or environmental causes.
Cryopreservation: a process where eggs, sperm or embryos are preserved by cooling to a very low temperature.
Cryoprotectant: a substance added to cells which reduces damage during freezing and thawing.
Culture medium: a solution in which cells can be grown in-vitro.
D
Deletion: also known as chromosomal deletion, is the loss of a part of a chromosome. Deletions may be small and involve only a single DNA base, or may be large and involve many genes.
Diploid: a cell with two sets of chromosomes, one from the mother and other one from the father. All human cells are diploid, except eggs and sperm which have only one set of chromosomes (haploid) as a result of meiosis.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): the basic biological molecule of heredity, carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all organisms.
Down syndrome: a congenital abnormality caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21 (Trisomy 21). It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability, and characteristic facial features. The parents of the affected individual are usually healthy and do not have Down syndrome. The probability of a woman carrying a Down syndrome baby is associated with increasing maternal age.
Duplication: also known as chromosomal / gene duplication, is any duplication of a region of DNA that contains a gene. As a result, there are two identical copies of the gene or part of the gene.
E
Ectopic pregnancy: a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo implants at a site other than the uterine cavity. An ectopic pregnancy most often occurs in the fallopian tube, and is also called a tubal pregnancy.
Egg: see oocyte.
Embryo: an early stage of development of an organism / human. A fertilized egg undergoes cell division to form an embryo. From this point until the ninth week after conception, the developing human is typically referred to as an embryo. After the ninth week, it is then referred to as a fetus.
Endometriosis: the presence of endometrial cells at sites other than the lining of the uterus, such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and pelvic peritoneum.
F
Fertilization: the process by which the male gamete (sperm) and the female gamete (egg / oocyte) unite to form a zygote.
Fetus: also known as foetus, is the unborn offspring of human that develops from an embryo.
Follicle: also known as ovarian follicle, is a roughly spheroid cellular aggregation found in the ovaries, each with the potential to release an egg (oocyte) at ovulation for fertilization.
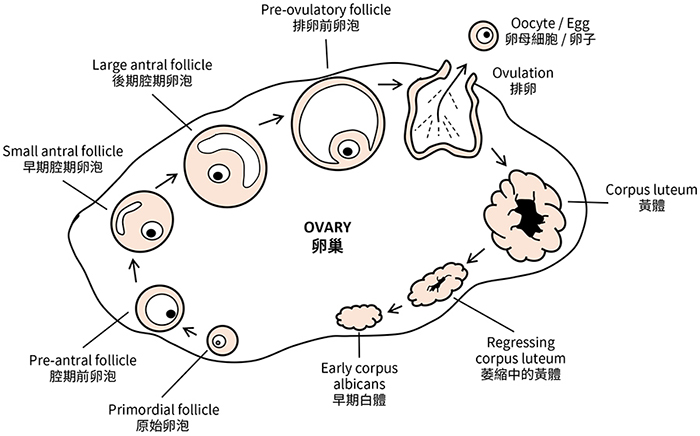
Follicular development
 scroll right to see more
scroll right to see more
G
Gamete: the male and female sex cells, i.e. the egg and the sperm.
Gene: the basic unit of genetic information, composed of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The specific DNA sequence of each gene encodes the synthesis of different gene products, which determine physical characteristics of individuals or control the various activities of the human body.
Genetic testing: a type of medical test that identifies changes in chromosomes or genes, including changes in chromosome structure, DNA sequence, DNA mutation or gene expression level. The results of a genetic test can confirm or rule out a suspected genetic condition or help determine a person's chance of passing on a genetic disorder.
H
Haploid: describes a cell that contains only one set of chromosomes. In human, only the gametes (eggs and sperm) are haploid.
Heterozygote: an individual in whom the maternal and paternal versions (alleles) of a gene are different.
Homozygote: an individual in whom the maternal and paternal versions (alleles) of a gene are the same.
Hyperstimulation: see ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
I
Infertility: failure to conceive after regular unprotected intercourse for a year.
Insertion: is the addition of one or more genes into a DNA sequence.
Intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI): the injection of a single sperm into the cytoplasm of an egg.
Intra-uterine insemination (IUI): an assisted reproduction technique in which a prepared specimen of semen is injected by means of a cannula through the cervix, and directly into the uterine cavity.
Inversion: is a chromosomae rearrangement in which a segment of a chromosome is reversed end to end, hence reversing the order of genes on this segment of the chromosome.
In-vitro fertilization (IVF): also known as test tube baby, is an assisted reproductive technology procedure in which mature eggs are collected (retrieved) from ovaries and fertilized by sperm in a laboratory (in-vitro). The fertilized eggs are cultured in the laboratory between two to six days to become embryos, and are then transferred to a uterus.
K
Karyotype: a description of the chromosome count of an individual.
Karyotyping: is a laboratory technique by which photographs of chromosomes are taken in order to determine the chromosome composition of an individual.
L
Luteal phase: The second half of the menstrual cycle, from the day of ovulation to the day before the next menstruation.
Luteal phase defect: also known as luteal phase deficiency, characterized by a shorter than normal luteal phase duration, or a lower than normal progesterone hormone level in the luteal phase, or both. It is generally believed that luteal phase defect will affect the implantation of embryos.
M
Menstruation: also known as a period, is the regular discharge of blood and mucosal tissue (known as menses) from the inner lining of the uterus through the vagina in response to cyclical rise and fall of hormones in a physiological cycle.
Miscarriage: also known as spontaneous abortion or pregnancy loss, is the natural death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently, usually before 20 weeks of gestation.
Monosomy: is a form of aneuploidy with the presence of only one chromosome from a pair.
Mosaicism: the coexistence of genetically different cell populations in a single individual.
Multiple pregnancy: a pregnancy in which two or more fetuses co-exist in the uterus.
Mutation: is a permanent change in a DNA sequence that makes up a gene. Mutations may not produce any discernible changes. If they make a gene function improperly thus causing a disease, this disease is then called a genetic disorder.
N
Necrozoospermia: a condition in which all sperm in the ejaculated semen are dead.
Non-obstructive azoospermia: no sperm in the ejaculate due to failure of spermatogenesis in the testicles, but the sperm ducts are not blocked.
O
Obstructive azoospermia: no sperm in the ejaculate due to bilateral obstruction in the sperm ducts, but spermatogenesis is normal.
Oligo-astheno-teratozoospermia (OAT): is a condition that includes oligozoospermia (low number of sperm), asthenozoospermia (poor sperm movement), and teratozoospermia (abnormal sperm shape).
Oligozoospermia: low sperm concentration in the semen.
Oocyte: also known as an egg, the female gamete.
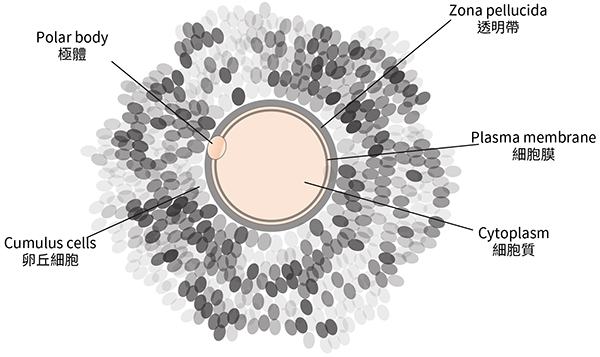
A mature oocyte
 scroll right to see more
scroll right to see more
Ovarian stimulation: the use of fertility drugs to promote the growth of multiple follicles.
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS): refers to an exaggerated response to ovarian stimulation hormones. It usually occurs in women taking gonadotropin hormone injections to stimulate the development of eggs in the ovaries.
Ovary: an organ found in the female reproductive system that produces an egg.
P
Pre-implantation genetic test (PGT): a technique by which embryos fertilized in-vitro are tested for specific genetic disorders before transfer into a uterus. Transfer of an affected embryo is thus avoided.
R
Reciprocal translocation: a type of chromosomae rearrangement involving the exchange of chromosome segments between two different chromosomes.
Robertsonian translocation: a type of chromosomae rearrangement that is formed by fusion of the whole long arms of two acrocentric chromosomes (chromosomes with the centromere near the very end).
S
Semen analysis: the analysis of seminal fluid and the sperm contained therein. It is usually done to help evaluate male fertility, whether for those seeking pregnancy or verifying the success of vasectomy. The technique and range of normal values have been standardized by the World Health Organization.
Sex chromosome: the X and Y chromosomes which determine the sex of an individual.
Spermatozoa: also known as sperm, the male gamete.
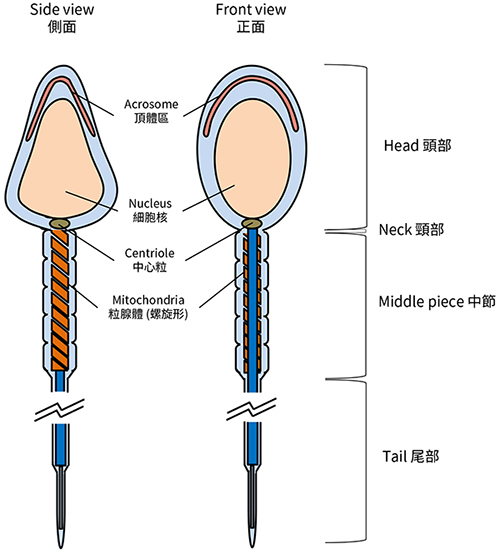
Spermatozoa structure
 scroll right to see more
scroll right to see more
Strict criteria: also known as Kruger criteria, is a highly specialized and strict method of defining sperm morphology (size and shape) described by Kruger, in which minute irregularities are considered as abnormal. WHO laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen has adopted the Kruger criteria in the 2010 version, and a normal semen sample will thus contain 4% or more normal forms according to the strict criteria.
Surgical sperm retrieval: a surgical procedure to collect sperm from men who have no sperm in their semen (azoospermia) for use in assisted reproductive technology treatments.
T
Teratozoospermia: also known as abnormal sperm morphology, is the presence of a high proportion of abnormally shaped spermatozoa in the semen.
Testicular sperm extraction (TESE): a surgical procedure of removing a small portion of tissue from the testicle and extracting any viable sperm for use in in-vitro fertilisation (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
Testis: an organ found in the male reproductive system that produces sperm.
Translocation: also known as chromosomal translocation, a condition caused by two breakages in two chromosomes, followed by an exchange and then a rejoining of the broken ends to produce a new chromosomal arrangement.
Triploidy: a chromosomal disorder in which a fetus has three copies of every chromosome instead of the normal two.
Trisomy: is a form of aneuploidy in which there are three copies of one particular chromosome.
Trophoectoderm: the outer single-cell layer of a blastocyst.
U
Ultrasound: also known as sonogram, is a procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to create an image of structures inside the body.
Uterus: also known as a womb, the uterus is where a fetus (unborn baby) develops and grows inside the mother’s body.
V
Vagina: is part of the female genital tract that connects the uterus to the outside world, and is the birth canal for the delivery of a baby.
Vasectomy: also known as male sterilization, a surgical procedure to achieve permanent contraception by cutting both vasa deferentia (sperm ducts).
Vitrification: a method of cryopreservation which uses a high concentration of cryoprotectant to replace the water in the cells in a short time, followed by rapid cooling to turn the cytoplasm into a glass-like structure, thereby avoiding ice crystal formation and any damaging effect on the cells.
W
World Health Organization (WHO): established in 1948, the specialized agency of health of the United Nations and the largest public health organization in the world.
X
X chromosome: one of the two sex-determining chromosomes. The presence of two X chromosomes determines that an individual is female. The presence of an X chromosome and an Y chromosome is male.
Y
Y chromosome: one of the sex-determining chromosomes. The presence of a Y chromosome causes a fetus to develop as a male who thus has an XY karyotype.
Z
Zona pellucida: is a glycoprotein layer surrounding the plasma membrane of an oocyte.
Zygote: the fertilized oocyte.